Quality of Service
Quality of Service
Network Services are considered end-to-end, this means from a Terminal Equipment (TE) to another TE. An End-to-End Service may have a certain Quality of Service (QoS) which is provided for the user of a network service. It is the user that decides whether he is satisfied with the provided QoS or not.
To realise a certain network QoS a Bearer Service with clearly defined characteristics and functionality is to be set up from the source to the destination of a service.
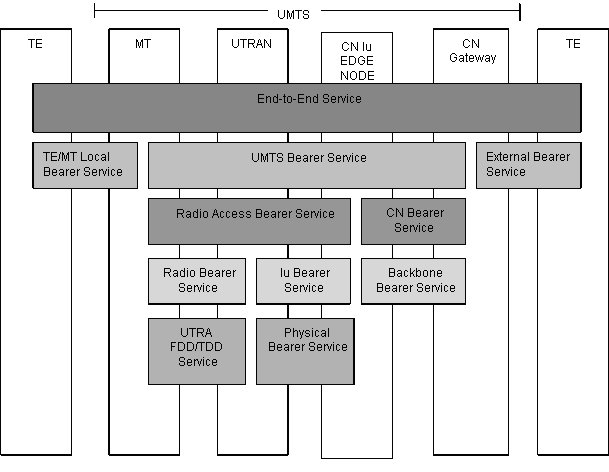
A bearer service includes all aspects to enable the provision of a contracted QoS. These aspects are among others the control signalling, user plane transport and QoS management functionality. A UMTS bearer service layered architecture is depicted below, each bearer service on a specific layer offers it's individual services using services provided by the layers below.
There are four different QoS classes:
Network Services are considered end-to-end, this means from a Terminal Equipment (TE) to another TE. An End-to-End Service may have a certain Quality of Service (QoS) which is provided for the user of a network service. It is the user that decides whether he is satisfied with the provided QoS or not.
To realise a certain network QoS a Bearer Service with clearly defined characteristics and functionality is to be set up from the source to the destination of a service.
A bearer service includes all aspects to enable the provision of a contracted QoS. These aspects are among others the control signalling, user plane transport and QoS management functionality. A UMTS bearer service layered architecture is depicted below, each bearer service on a specific layer offers it's individual services using services provided by the layers below.
|
QoS Architecture
There are four different QoS classes:
Comments
Post a Comment